How Tea Seed Oil Processing Promotes Profitability
Seeking high-value oils? Tea seed oil demand is rising but seems complex. We clarify its potential and processing needs for your investment strategy.
Tea seed oil, from Camellia seeds, is rich in oleic acid (“Oriental Olive Oil”) . Its growing demand in food and cosmetics makes it a valuable investment, requiring specific processing expertise.

This unique oil, often called “Oriental Olive Oil,” presents a significant market opportunity. However, understanding the raw material and its processing is crucial before investing. Let’s explore the details.
What Makes Tea Seeds Unique for Oil Extraction?
Poor tea seed quality ruins yield and oil value. Unsure how to select and handle them? We highlight critical factors affecting your output.
Tea seeds require full maturity, specific dryness (8-10% moisture), thorough cleaning, and freshness. Quality directly impacts oil yield, FFA levels, peroxide value, flavor, and color, making careful selection crucial.
Processing tea seeds effectively starts with understanding their specific needs. Unlike more common oilseeds, certain characteristics demand special attention.
Key Quality Factors for Tea Seeds
The quality of your input tea seeds directly translates to the quality and quantity of your output oil. At Zhengzhou Fude Machinery, we emphasize starting right.
| Factor | Importance | Why Crucial for Pressing |
|---|---|---|
| Maturity | Essential for highest oil content and best quality. | Immature seeds yield less oil, have high moisture. |
| Dryness | Critical (8-10% moisture). | Too wet = slipping, low yield; Too dry = brittle. |
| Cleanliness | Vital for equipment life and oil purity. | Impurities cause wear, contaminate oil. |
| Freshness | Prevents mold (aflatoxins) and degradation (high FFA). | Moldy seeds yield unsafe, poor-tasting oil. |
| Variety | Different Camellia species/varieties have varying oil yields/flavors. | Choose varieties known for high oil content (e.g., C. oleifera). |
Using fully mature, correctly dried (a crucial step often requiring mechanical dryers), clean, and fresh seeds is non-negotiable for producing high-quality tea seed oil and ensuring smooth operation of your pressing equipment.
What Are the Essential Steps for Tea Seed Oil Extraction?
Confused about the tea seed oil process? Missing steps leads to poor results and wasted investment. We outline the necessary stages from raw seed to crude oil.
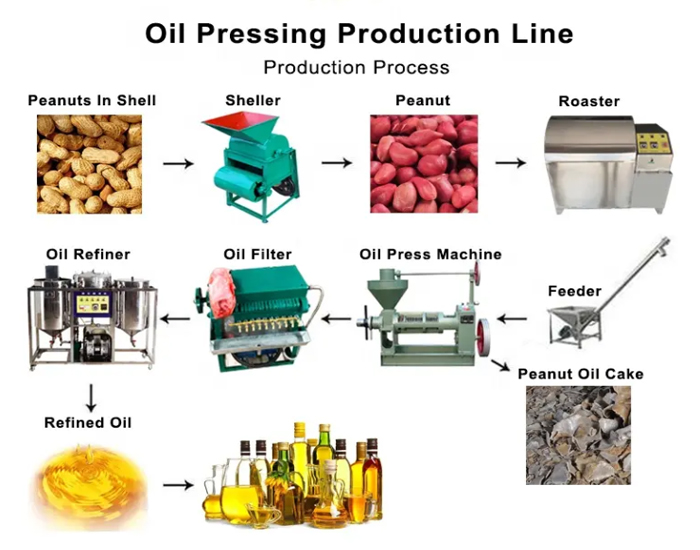
Key steps are: drying seeds to 8-10% moisture, efficient shelling (critical!), kernel-shell separation, optional crushing/rolling, optional cooking (for hot pressing), pressing (using suitable equipment), and initial filtration of crude oil.
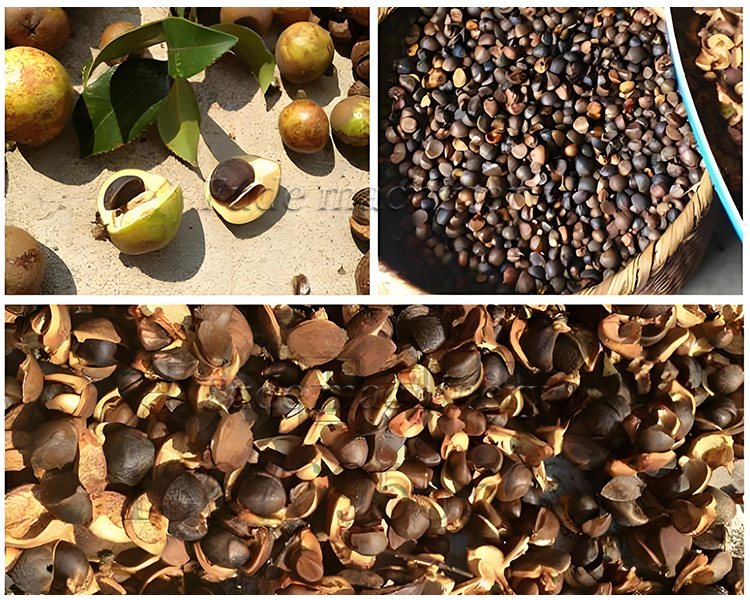

Extracting tea seed oil involves several stages, each vital for maximizing yield and quality. Skipping or improperly performing steps can significantly compromise the outcome.
Tea Seed Oil Extraction Workflow
A typical process flow, using equipment solutions provided by Zhengzhou Fude Machinery, looks like this:
| Step | Purpose | Fude Machinery Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Drying | Achieve optimal moisture (8-10%) for pressing and storage. | Mechanical dryers available. |
| Shelling | Remove hard, abrasive shell to protect press and improve yield. | Specialized tea seed shellers. |
| Kernel-Shell Separation | Remove shell fragments from kernels efficiently. | Screening or aspiration equipment. |
| Crushing/Rolling (Opt.) | Increase surface area, break cells for better oil release. | Crushers, Flaking Mills. |
| Cooking (Hot Pressing) | Further break cells, reduce viscosity, denature protein. | Cookers/Steamers integrated with presses. |
| Pressing | Mechanically separate oil from solids. | Heavy-duty screw presses, Hydraulic presses. |
| Filtration | Remove solid impurities (foots) from crude oil. | Plate & frame filters, pressure leaf filters. |
| Refining (Optional) | Degumming, deacidification, decolorization, deodorization for standard oil. | Complete refining lines available. |
Two steps deserve special emphasis: Drying is critical to reach the target moisture content precisely. Shelling is extremely important because the hard shell causes severe wear on pressing equipment if not removed effectively. Our specialized shellers are designed for this task.
Cold Pressing or Hot Pressing: Which is Better for Tea Seed Oil?
Choosing the wrong pressing method wastes potential. Cold or hot pressing for tea seed oil? We compare them to match your product goals and market needs.
Cold pressing preserves natural flavor and nutrients but yields less oil. Hot pressing maximizes yield with a roasted flavor but loses some nutrients. Choose based on target market: high-end (cold) or yield-focused (hot).
Cold vs. Hot Pressing for Tea Seed Oil
Understanding the trade-offs helps you align your production with your market strategy.
| Feature | Cold Pressing (<60°C) | Hot Pressing (>100°C Cooking) |
|---|---|---|
| Goal | Preserve natural flavor, nutrients, color. | Maximize oil yield. |
| Yield | Lower (e.g., 30-38% from kernel). | Higher (e.g., 38-45% from kernel). |
| Flavor/Aroma | Natural, fresh, original seed taste. | Roasted, nutty aroma. |
| Nutrients | Better preservation (Vit E, squalene). | Some heat-sensitive nutrients lost. |
| Equipment | Hydraulic press, specialized low-temp screw press. | Screw press with cooker. |
| Raw Material | Requires very high quality, fresh seeds. | More tolerant, but quality still matters. |
Cold pressing caters to the premium market demanding natural, nutrient-rich oils. It requires top-quality raw materials and specific equipment like our hydraulic presses or low-temperature screw models. Hot pressing, using our screw presses paired with cookers, focuses on achieving the highest possible oil yield, suitable for mass-market edible oils or oils intended for further refining. Your product positioning dictates the best approach.
Choosing the Right Press for Tea Seeds
Consider the scale and type of operation when selecting a press from Zhengzhou Fude Machinery.
| Press Type | Advantages | Disadvantages | Fude Machinery Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Screw Press | Continuous, high capacity, suitable for hot/cold (specific models). | Requires excellent shelling; high wear on parts if shells present. | Heavy-duty models with hardened alloy steel parts; specify tea seed use. |
| Hydraulic Press | Excellent for cold pressing quality; gentler; less pre-treatment sensitive. | Batch operation, lower capacity, higher labor intensity. | Ideal for small-scale, high-quality cold press focus. |
How Much Oil Can Be Extracted From Tea Seeds and How to Increase Yield?
Expect 30-38% oil yield from kernels via cold pressing, and 38-45% via hot pressing. Improve yield with high-quality, mature, correctly dried seeds, thorough shelling, optimal pre-treatment (crushing/cooking), and efficient, well-maintained presses.


Achieving the best possible oil yield is key to profitability. Several factors influence how much oil you can recover from your tea seeds.
Maximizing Tea Seed Oil Yield
While theoretical oil content is fixed, practical yield depends on optimizing each process step.
| Method | Action | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Material Selection | Use mature, high-oil varieties; avoid mold. | Higher starting oil content potential. |
| Drying Control | Achieve optimal moisture (8-10%). | Prevents slipping or powdering; aids release. |
| Thorough Shelling | Remove as much hard shell as possible. | Less non-oil material, better pressing contact. |
| Pre-treatment | Crush/roll kernels; optimize cooking (hot press). | Better cell rupture, lower oil viscosity. |
| Press Selection/Operation | Use suitable heavy-duty press; optimize pressure/speed settings. | Efficient mechanical oil separation. |
| Maintenance | Regularly inspect and replace worn screw/cage bars. | Maintains optimal pressure and efficiency. |
| Second Pressing (Opt.) | Repress the first-press cake. | Recovers some additional residual oil. |
| Solvent Extraction | (Large scale) Extract residual oil from cake using solvents. | Highest possible total yield (requires plant). |
Focusing on raw material quality, precise drying, and efficient shelling provides the foundation. Using the right Fude Machinery press correctly and maintaining it well ensures you extract the maximum possible oil mechanically. For very large scales, pre-pressing followed by solvent extraction achieves the absolute highest recovery, a solution we can also design.
It starts with excellent raw materials. Each subsequent step – from pre-treatment using reliable Fude Machinery equipment to careful pressing, immediate filtration, and proper storage – aims to preserve that initial quality. Maintaining clean equipment is paramount to prevent contamination. Regular testing verifies that your process consistently delivers oil meeting required specifications (e.g., low acid value, low peroxide value).
What Common Problems Occur During Tea Seed Oil Processing and How to Fix Them?
Facing issues like low yield or machine wear? Frustrated by processing problems during production? We identify common tea seed oil challenges and offer practical solutions.
Common issues include low yield (check moisture, shelling, wear), high acid value (check raw materials, storage, hygiene), turbidity (improve filtration), rapid wear (check cleaning, shelling), and scorched flavor (control cooking parameters).

Even with good equipment, processing tea seeds can present challenges. Recognizing and addressing them quickly is crucial for smooth operation.
Many issues trace back to raw material quality (moisture, cleanliness, freshness) or incomplete shelling. Ensuring these are correct is the first line of defense. Regular maintenance, including timely replacement of wear parts like screw elements and cage bars (available from us), is essential for consistent performance and preventing yield loss or equipment damage.
What Are the High-Value Uses of Tea Seed Cake?
Don’t discard tea seed cake as simple waste! It’s more valuable than you think due to unique compounds. Discover its uses beyond typical animal feed applications.
Tea seed cake contains natural tea saponin, making it useful beyond basic feed. Applications include natural pesticides/molluscicides (fish farming, agriculture), organic fertilizer, and potentially the extraction of valuable saponins themselves.

Unlike many other oilseed cakes primarily valued for protein, tea seed cake (also called tea dregs or tea meal) possesses unique properties thanks to its natural saponin content.
Utilizing Tea Seed Cake
This by-product offers several potential revenue streams:
| Use | Basis | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Natural Pesticide/Molluscicide | Tea Saponin content | Effectively kills unwanted pests/snails (e.g., cleaning shrimp ponds, protecting crops, golf course maintenance). |
| Organic Fertilizer | Organic matter, NPK | Improves soil structure and fertility; saponin may have soil benefits. |
| Animal Feed (Limited) | Protein, Fiber | Use requires caution due to saponin toxicity to some animals (especially fish); suitability needs verification. |
| Saponin Extraction | High Saponin content | Potential source for industrial/cosmetic saponins (requires further specialized processing). |
Conclusion
Tea seed oil offers unique quality and market potential. Success hinges on understanding the material, using proper pre-treatment, and employing robust, suitable equipment. We provide reliable solutions.
Related recommendations
-
How much is the price of a small oil press in 2024
422Zhengzhou Fude Machinery integrates production, manufacturing, and sales, with rich experience in the oil press industry, complete equipment, and discounted prices.
View details -
What is the difference between hydraulic oil press and screw oil press
162Hydraulic oil press and spiral oil press are two common oil crop oil pressing equipment, which have significant differences in pressing principles, applicable oil materials, oil yield and efficiency, equipment advantages and disadvantages, etc.
View details -
What key details are overlooked in screw presses?
32Understanding Pressing TemperaturesWhy Temperature Control MattersWhy is Raw Material Pre-treatment a Hidden Profit Center?Key Pre-treatment StepsThe Importance of Cooking/ConditioningIs "Pressing Until Dry" the Best Strategy for Screw Presses?Mat...
View details -
The difference between cold pressing and hot pressing of spiral oil press
298Spiral oil press is suitable for pressing various types of oil
View details
 Oil Press Equipment and Oil Refining Machinery for Sale – Start Your Oil Press Business
Oil Press Equipment and Oil Refining Machinery for Sale – Start Your Oil Press Business




HelloPlease log in